
Variable stability, dependent on the status of medial structures (malleolus/ deltoid ligament) and syndesmosis may require open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) Tibiofibular syndesmosis usually intact, but widening of the distal tibiofibular joint (especially on stressed views) indicates syndesmotic injuryĭeltoid ligament may be torn, indicated by widening of the space between the medial malleolus and talar dome Usually stable if medial malleolus intact treat with CAM Walker or Moon Boot with crutches and weight bear as tolerated with them for 6 weeksĭistal extent at the level of the syndesmosis (trans-syndesmotic) may extend some distance proximally
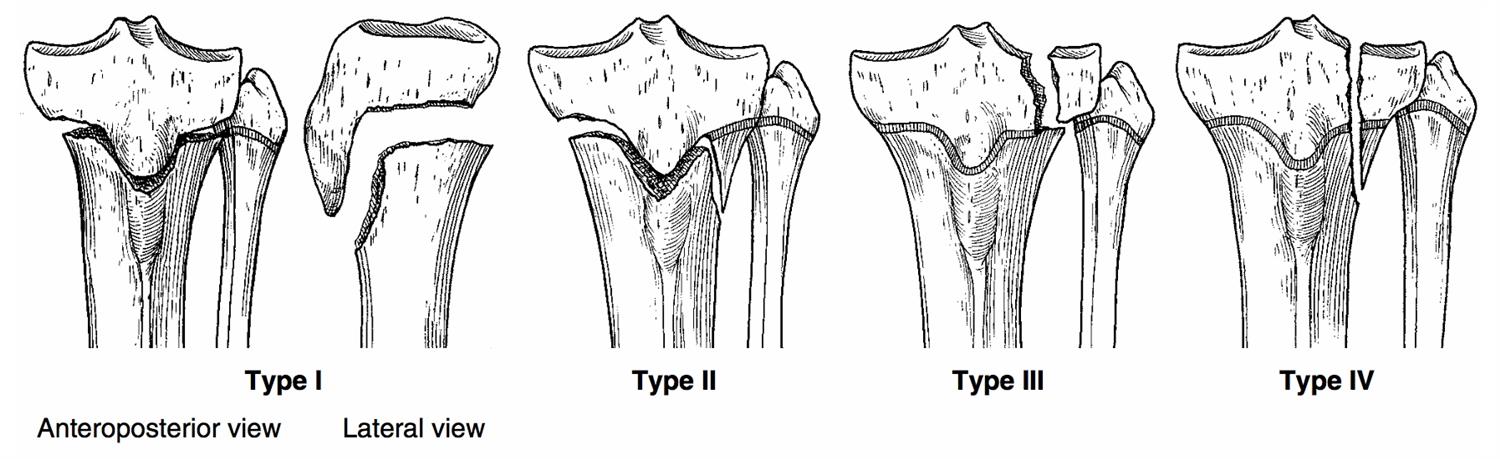
White arrow points to metaphyseal fracture and yellowĪrrow to a fracture of the distal tibial epiphysis in this Salter-Harris IV fracture of the ankle.Below the level of the syndesmosis (infrasyndesmotic) Closure of only a portion of the plate resulting in angular deformity.Primary complication is growth plate disturbance.Greater risk for complication comes with fracture of distal tibia followed by distal femur.In general, the higher the number, the more likely the complication so that Salter-Harris types Iv and V have the highest associated complications.Ultrasound can be helpful in infants whose cartilage has not yet ossified.CT with multiplanar reconstruction has been used in problem cases.Conventional radiography remains study of first choice.Depending on the type of fracture, some displacement of the epiphysis or corner sign (Thurston-Holland fragment).Structures involved in Salter-Harris fractures These injuries have the worst prognosis of the Salter-Harris fractures.Initial diagnosis may be difficult and not made until complication of growth disturbance at epiphyseal plate occurs resulting in angular deformities.Compression or crushing injury of epiphyseal plate.Since these fractures involve the growing layer of cartilage, growth disturbance can result.Since it, too, involves the epiphysis, the articular cartilage can be damaged.Involves the epiphyseal plate, metaphysis and epiphysis.A Tillaux fracture of the ankle is a Salter-Harris III fracture.

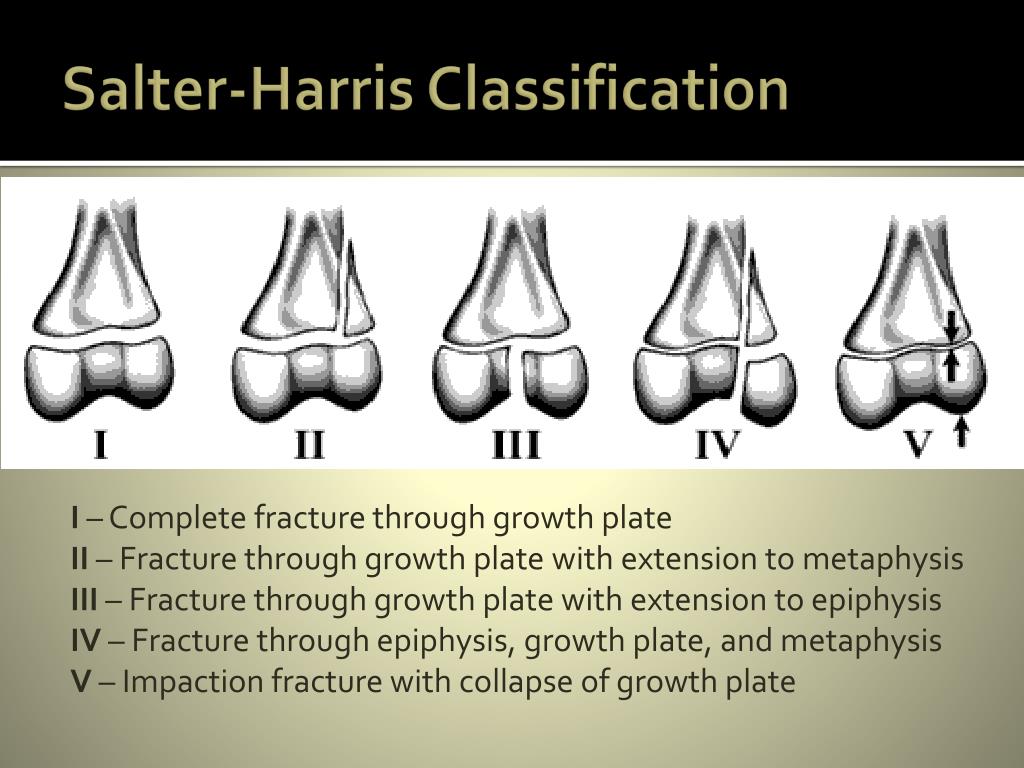
Involves the epiphyseal plate and the epiphysis itself.Small corner of metaphysis that is usually fractured produces the “corner sign”.Involves both the epiphyseal plate and the metaphysis.Most common Salter-Harris fracture -85%.Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) is an example of a Salter-Harris I fracture.May be difficult to diagnose unless there is visible displacement of the epiphysis on the metaphysis.Occurs through the hypertrophic zone of the epiphyseal plate.All such these fractures, by definition, involve or extend through the epiphyseal plate so that all such fractures occur in children before the epiphyseal plate closes.The Salter-Harris classification is a means of categorizing epiphyseal plate fractures and provides clues to their prognosis.The epiphyseal plate ( physis or growth plate) is the weakest part of the bone to shearing injuries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
